一、Linux安装MySQL
# 一、Linux安装MySQL
# 1 Linux在线安装MySQL5.7
# 1.1 删除已有的相关包
在安装前需要确定现在这个系统有没有 MySQL,如果有那么必须卸载。尤其是新的 CentOS 7 系统,它自带mariaDB数据库,所以需要卸载掉。
查找已安装的MySQL软件包:
rpm -qa|grep mysql
# 1.2 CentOS7下还需要查找是否存在mariadb包:
rpm -qa|grep mariadb
如果输入上述两个命令后都输出存在有包,则需要执行删除命令。 例如,前两步中终端输出了“mysql-libs-5.1.73-1.el6.x86_64”和“mariadb-libs-5.5.56-2.el7.x86_64”,则:
rpm -e --nodeps mysql-libs-5.1.73-1.el6.x86_64
rpm -e --nodeps mariadb-libs-5.5.56-2.el7.x86_64
# 1.2 提升权限
由于 MySQL 安装过程中,会通过 MySQL 用户在 /tmp 目录下新建 tmp_db 文件,所以需要给 /tmp 目录较大的权限:
chmod -R 777 /tmp
# 1.3 检查依赖
这一步需要检查系统中是否存在一些安装MySQL时需要的依赖库。因为考虑到大家有些是在虚拟机上安装的Linux系统。如果安装系统的时候用的是最小安装等原因,可能就不存在这些库。
执行两个查询命令看是否存在依赖库:
rpm -qa|grep libaio
rpm -qa|grep net-tools
如果不存在则需要安装:
yum -y install libaio net-tools
# 2 准备好安装包
MySQL 阿里云盘 (opens new window)
mysql-community-common-5.7.16-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
mysql-community-libs-5.7.16-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
mysql-community-client-5.7.16-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
mysql-community-server-5.7.16-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
这 4 个安装包通过 Xtfp 复制到 /opt下:
# 3 开始安装
使用 rpm 命令按顺序依次安装 4 个包:
rpm -ivh mysql-community-common-5.7.16-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh mysql-community-libs-5.7.16-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh mysql-community-client-5.7.16-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh mysql-community-server-5.7.16-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
执行 " mysqladmin –version " 命令,类似 " java -version " 如果输出版本消息,即为安装成功。
# 4 相应配置
# 4.1 初始化 MySQL
MySQL 5.7下载完后需要手动初始化:
mysqld --initialize --user=mysql
# 4.2 查看密码
查看并记住初始密码,“root@localhost:” 后面的就是初始化密码,要记下来,后面连接数据库会用到。
cat /var/log/mysqld.log | tail -n 10
# 4.3 启动 MySQL 服务
启动服务
systemctl start mysqld.service
启动MySQL报错
service mysqld start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start mysqld.service
Job for mysqld.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See "systemctl status mysqld.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.
journalctl -xe 分析错误
解决方法
chown mysql:mysql -R /var/lib/mysql
# 4.4 关闭服务
systemctl stop mysqld.service
# 4.5查看服务状态
systemctl status mysqld
# 4.6 查看服务是否自启动
systemctl list-unit-files|grep mysqld.service
# 4.7 设置自启动
systemctl enable mysqld.sercice
# 4.8 首次登录
mysql -uroot -p
# 4.9 修改密码
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';
# 4.10 重启MySQL
systemctl restart mysqld
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43280818/article/details/115625306 参考链接
# 5 配置/etc/my.conf
bind-address=192.168.104.128
port=3308
# 修改本地root密码
- mysql安装完成之后,在/var/log/mysqld.log文件中给root生成了一个默认密码。通过以下命令找到密码:
sudo grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
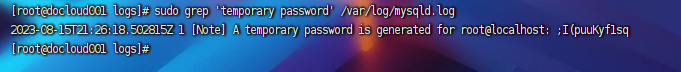
- 登录MySQL,记得使用刚才找到的密码
mysql -u root -p
- 设置新密码
set password for 'root'@'localhost'=password('MyNewPass4!');
- 修改root账户名
update mysql.user set user = 'myRoot' where user = 'root';
- 修改远程登录密码
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON . TO 'myRoot'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'myRoot用户的密码' WITH GRANT OPTION;
- 刷新MySQL的系统权限相关表,否则会出现拒绝访问
flush privileges;
# 二、Linux离线安装MySQL
linux 离线安装MySQL
# 1) 卸载CentOS7系统自带mariadb
# 查看系统自带的Mariadb
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa|grep mariadb
mariadb-libs-5.5.64-1.el7.x86_64
# 卸载系统自带的Mariadb
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -e --nodeps mariadb-libs-5.5.64-1.el7.x86_64
# 删除etc目录下的my.cnf(如果有就删除,可以执行试一下,没有会提示你的)
[root@localhost ~]# rm /etc/my.cnf
# 2) 检查mysql是否存在
# 检查是否已经安装
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa | grep mysql
# 如果什么都没有返回 空的 说明啥也没安 可以继续安装
# 3) 检查mysql的用户和组是否存在如果不存在就创建
# 检查有没有mysql用户
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd | grep mysql
# 检查有没有mysql组
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/group | grep mysql
# 查询全部用户
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd|grep -v nologin|grep -v halt|grep -v shutdown|awk -F ":" '{print $1 "|" $3 "1" $4}' | more
# 如果不存在就创建mysql用户
# 创建mysql用户组
[root@localhost ~]# groupadd mysql
# 创建一个用户名为mysql的用户,并加入mysql用户组
[root@localhost ~]# useradd -g mysql mysql
# 设置mysql的密码 000000
[root@localhost ~]# passwd mysql
更改用户 mysql 的密码 。
新的 密码:
无效的密码: 密码是一个回文
重新输入新的 密码:
passwd:所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。
# 4) 下载MySQL的离线安装包
官网下载地址:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/5.7.html#downloads
版本选择,可以选择一下两种方式:
1)使用Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Select Version: 5.7.* (因为更新的缘故具体细节版本可自行查看)
Select Operating System: Red Hat Enterprise Linux / Oracle Linux
Select OS Version: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 / Oracle Linux 7 (x86, 64-bit)
列表中下载:
Compressed TAR Archive:(mysql-5.7.25-el7-x86_64.tar.gz) 【本文中使用的是这个版本】
2)使用Linux - Generic
Select Version: 5.7.* (因为更新的缘故具体细节版本可自行查看)
Select Operating System: Linux - Generic
Select OS Version: Linux - Generic (glibc 2.12) (x86, 64-bit)
列表中下载:
Compressed TAR Archive:(mysql-5.7.25-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz)
# 5) 上传MySQL的离线安装包并解压进行传统配置
# 将mysql解压到 /usr/local 下
[root@localhost mysoft]# tar -zxvf mysql-5.7.29-el7-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
# 创建软连接
[root@localhost local]# ln -s mysql-5.7.29-el7-x86_64 mysql
# 修改目录与软件连的所属用户和组
[root@localhost local]# chown -R mysql:mysql mysql-5.7.29-el7-x86_64
[root@localhost local]# chown -h mysql:mysql mysql
# 创建mysql的数据目录
# 进入mysql(cd /usr/local/mysql)
[root@localhost local]# cd mysql
# 创建 data 目录
[root@localhost mysql]# mkdir data
# 目录赋权
[root@localhost mysql]# chown mysql:mysql ./data
# 6) 创建配置文件
[root@localhost local]# cd mysql
[root@localhost mysql]# vim my.cnf
(内容如下 : )
[mysql]
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
# set mysql client default chararter
default-character-set=utf8
[mysqld]
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
# set mysql server port
port = 3306
# set mysql install base dir
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
# set the data store dir
datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data
# set sql mode
sql_mode=STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
# set the number of allow max connnection
max_connections=200
# set server charactre default encoding
character-set-server=utf8
# the storage engine
default-storage-engine=INNODB
lower_case_table_names=1
max_allowed_packet=16M
explicit_defaults_for_timestamp=true
[mysql.server]
user=mysql
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
# 7) 开始安装MySQL
[root@localhost mysql]# cd /usr/local/mysql
[root@localhost mysql]# bin/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql/ --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data/
2020-02-12 15:14:15 [WARNING] mysql_install_db is deprecated. Please consider switching to mysqld --initialize
2020-02-12 15:14:20 [WARNING] The bootstrap log isn't empty:
2020-02-12 15:14:20 [WARNING] 2020-02-12T07:14:16.103773Z 0 [Warning] --bootstrap is deprecated. Please consider using --initialize instead
2020-02-12T07:14:16.104788Z 0 [Warning] Changed limits: max_open_files: 1024 (requested 5000)
2020-02-12T07:14:16.104795Z 0 [Warning] Changed limits: table_open_cache: 431 (requested 2000)
设置权限
[root@localhost mysql]# cp ./support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
[root@localhost mysql]# chown 777 my.cnf
[root@localhost mysql]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/mysqld
# 8) 启动MySQL
[root@localhost mysql]# mkdir -p /var/lib/mysql
[root@localhost mysql]# chown -R mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql
# 启动一次
[root@localhost mysql]# /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
ERROR! MySQL server PID file could not be found!
Starting MySQL.Logging to '/usr/local/mysql/data/localhost.localdomain.err'.
SUCCESS!
# 再启动一次
[root@localhost mysql]# /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
Shutting down MySQL.. SUCCESS!
Starting MySQL. SUCCESS!
# 9) 设置开机启动
[root@localhost mysql]# chkconfig --level 35 mysqld on
[root@localhost mysql]# chkconfig --list mysqld
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
mysqld 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关
[root@localhost mysql]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld
[root@localhost mysql]# chkconfig --add mysqld
[root@localhost mysql]# chkconfig --list mysqld
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
mysqld 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关
[root@localhost mysql]# service mysqld status
SUCCESS! MySQL running (60791)
# 10) 修改配置文件
[root@localhost mysql]# vim /etc/profile
添加一行 export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/mysql/bin
[root@localhost mysql]# source /etc/profile
# 11) 获取初始密码
获取初始密码
[root@localhost mysql]# cat /root/.mysql_secret
# Password set for user 'root@localhost' at 2020-02-12 15:14:15
Qba3P)r#ft_>
创建软连接
[root@localhost mysql]# ln -s /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock /tmp/mysql.sock
登录mysql
[root@localhost tmp]# mysql -uroot -p'Qba3P)r#ft_>'
修改密码
[root@localhost tmp]# mysql -uroot -p'Qba3P)r#ft_>'
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 2
Server version: 5.7.29
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> set PASSWORD = PASSWORD('000000');
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
检验密码是否成功
mysql> exit
Bye
[root@localhost tmp]# mysql -uroot -p000000
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.29 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
设置远程访问
[root@localhost tmp]# mysql -uroot -p000000
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.29 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '000000';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'localhost' identified by '000000';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)